For More Info!
Cloud Landing zone: An Efficient Framework for Large-Scale Cloud Migration
Table of Contents
Cloud migration can be a complex process, especially when an organization lacks expertise or resources for setting up a cloud environment effectively.
Managing a large cloud environment with numerous accounts (AWS) or subscriptions (Azure) can also be challenging.
The cloud landing zone is a strategic approach that addresses these challenges and streamlines the process of cloud migration. But what exactly is a cloud landing zone, and why do companies need it? Let’s explore this concept in detail.
1 - What Is a Cloud Landing Zone?
In essence, a cloud landing zone is a cloud adoption framework that enables organizations to carry out large-scale cloud migration efficiently and effectively.
By establishing initial parameters, a cloud landing zone ensures that applications and data are managed according to best practices in security and compliance. This framework sets the stage for an optimal cloud environment tailored to each organization’s needs.
2 - Cloud Adoption Framework - CAF
A landing zone in the Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF) model is a structured cloud environment that adheres to key design principles for scalability and security.
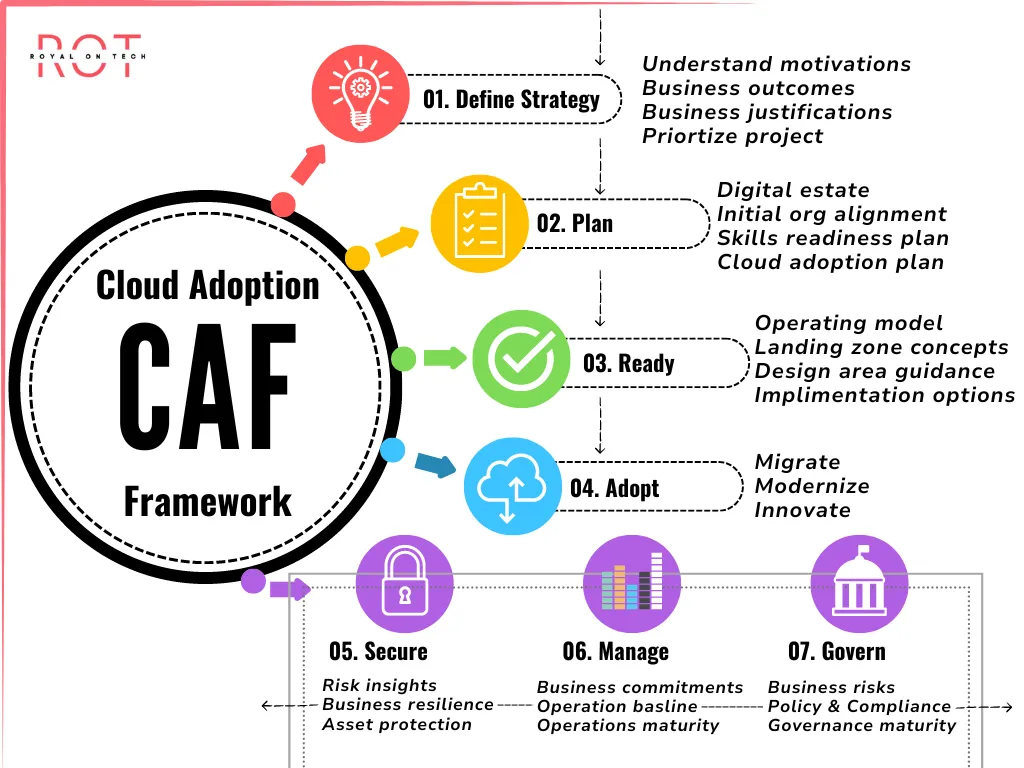
It provides a foundation for efficiently deploying workloads and applications while ensuring the architecture is well-designed and meets business needs, enabling organizations to make the most of cloud services.
The steps in the framework are as follows :
01. Define Strategy
This step involves determining what the organization wants to achieve with cloud adoption. This includes business outcomes and justifications for moving to the cloud.
02. Plan
This step involves planning for cloud adoption. This includes understanding the organization’s digital estate, aligning the organization for cloud adoption, and creating a skills readiness plan and a cloud adoption plan.
03. Ready
This step involves getting ready for cloud adoption. This includes creating an operating model, designing landing zone concepts, and creating design area guidance and implementation options.
04. Adopt
This step involves adopting cloud computing. This includes migrating workloads to the cloud, modernizing applications, and innovating with new cloud-based services.
05. Secure
This step involves securing cloud deployments. This includes understanding risk insights, business resilience, and asset protection.
06. Manage
This step involves managing cloud deployments. This includes establishing business commitments, understanding operational baselines, and achieving operations maturity.
07. Govern
This step involves governing cloud deployments. This includes establishing policies and compliance requirements, and achieving governance maturity.
3- Leading Cloud LZ's Providers
4 - Customizing the Cloud Landing Zones
Each organization has unique requirements, including different applications, compliance needs, and IT infrastructure.
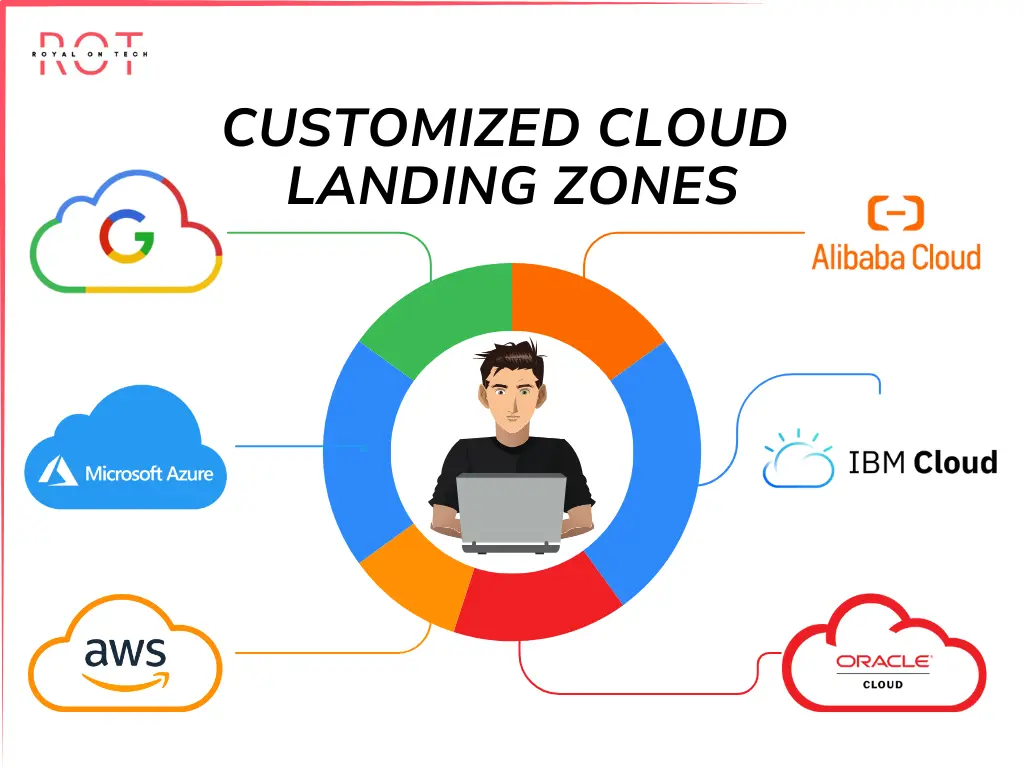
Therefore, a customized landing zone must be carefully designed to meet these specific needs.
Collaborating with cloud providers who have expertise in this area is essential to set up the landing zone correctly from the outset.
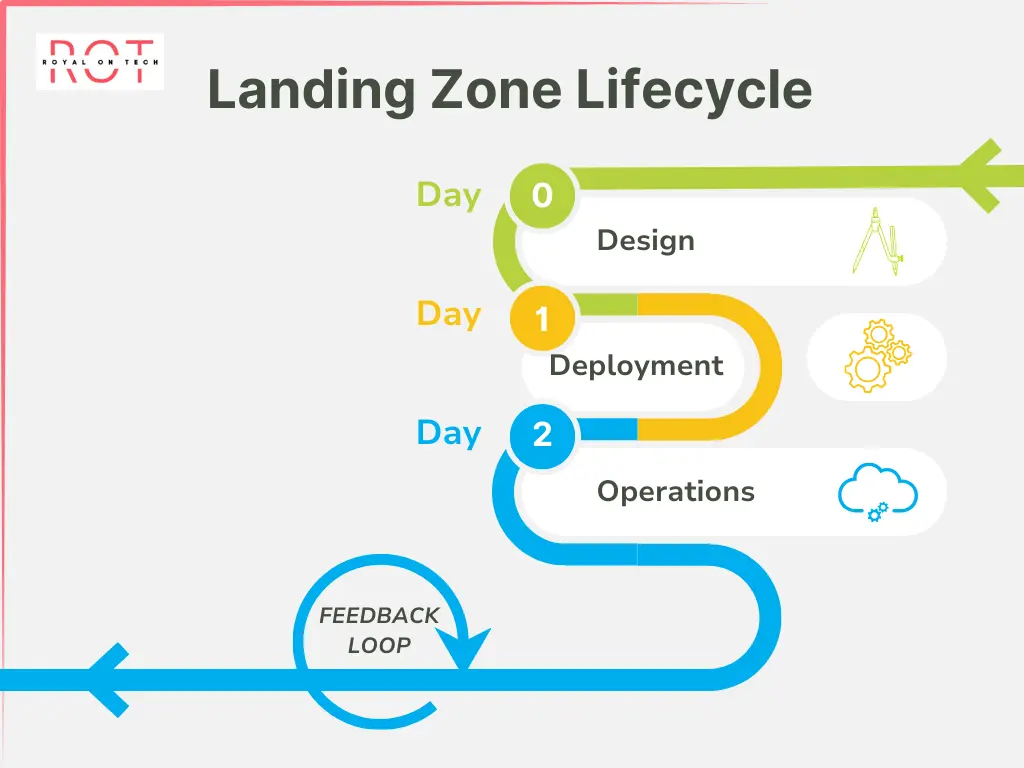
5 - Cloud Landing Zone Lifecycle
In the context of a cloud landing zone, “Day 0,” “Day 1,” and “Day 2” refer to specific phases in the lifecycle of establishing and managing the landing zone within a cloud environment. Here’s how these terms apply:
5.1
Cloud Landing Zone Lifecycle
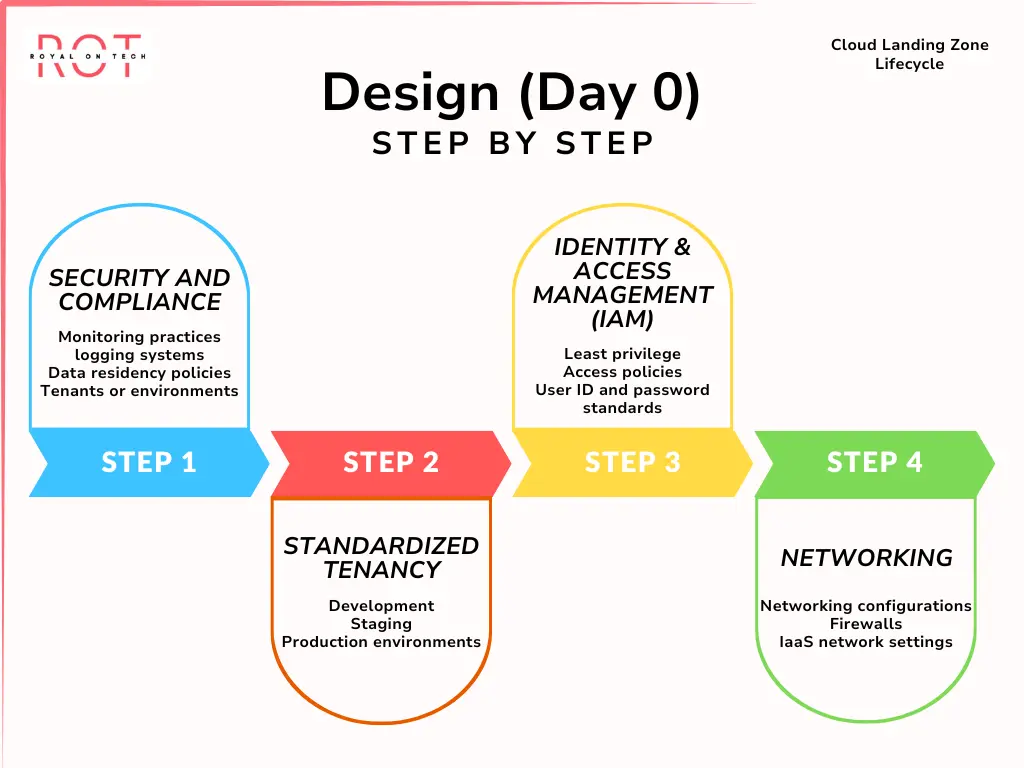
Design (Day 0)
Planning is crucial in this stage. Organizations must strategize and establish requirements such as security and compliance, workload management, performance, identity and access management, networking, high availability, and cost optimization. By creating a roadmap, you can avoid potential challenges in your cloud journey.
Design (Day 0) Explained
As you begin your adventure into the cloud, it’s important to plan and strategize your landing zones carefully. These landing zones act as the first step and crucial base of your cloud setup.
Let’s explore four important areas that a well-designed landing zone should cover:
Security and Compliance
- It’s important to streamline your security measures, monitoring practices, and logging systems. By centralizing these aspects, you can ensure that company-wide compliance requirements and data residency policies are adhered to. This approach enables the establishment of a baseline level of compliance across various tenants or environments.
Standardized Tenancy
- To promote consistency and efficiency, it’s beneficial to enforce tagging policies consistently across multiple cloud tenants. Additionally, offering standardized tenants tailored to different security profiles (such as development, staging, and production environments) helps maintain organization and clarity.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Implementing the principle of least privilege is key to enhancing security. This involves defining specific roles and access policies to restrict access to only what is necessary for each user. It’s also essential to establish uniform user ID configurations and password standards across all tenants.
Networking
- Establishing foundational networking configurations is vital for smooth operations. This includes setting up Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) network configurations, implementing firewalls, and configuring other basic networking parameters according to your requirements. Having these elements in place ensures a robust networking infrastructure within your cloud environment.
5.2
Cloud Landing Zone Lifecycle
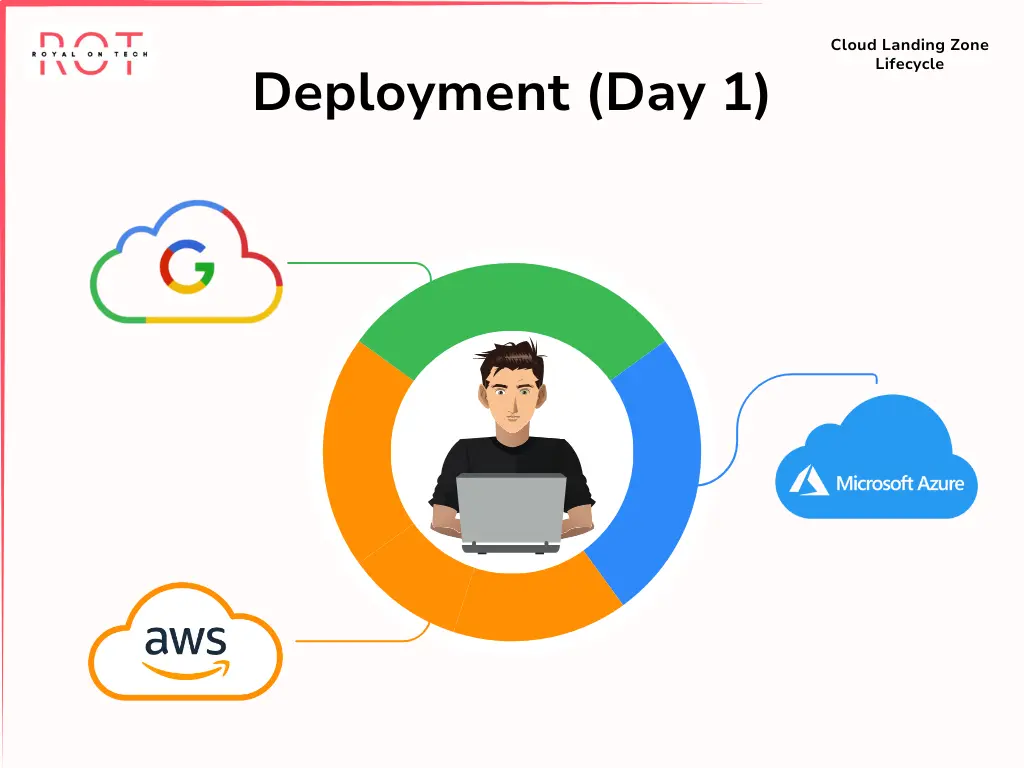
Deployment (Day 1)
- Once the design phase is complete, deployment begins. Different cloud service providers (CSPs) handle landing zones differently based on their cloud adoption frameworks. Choose a cloud landing zone service from top vendors like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) that aligns with your business needs.
Deployment (Day 1) Explained
During the initial deployment phase, known as Day 1, the focus is on tailoring and rolling out a landing zone based on the design and specifications outlined during the planning phase, Day 0. Different public cloud service providers approach the implementation of landing zones in varying ways.
Let’s examine the approaches of the three major cloud service providers:
Microsoft Azure
- Within Microsoft’s cloud platform, the Cloud Adoption Framework incorporates the concept of landing zones. A key tool for this is Azure blueprints, which allows users to select and configure migration landing zone blueprints within Azure to establish their cloud environments. Alternatively, third-party services like Terraform can also be utilized.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- AWS offers a solution simply known as AWS Landing Zone. This solution includes a pre-configured security baseline that sets up AWS services such as CloudTrail, GuardDuty, and Landing Zone Notifications. Additionally, it automates the setup of a landing zone environment, expediting cloud migrations. Depending on specific needs, AWS provides CloudFormation Templates for customizing and standardizing service or application architectures.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- GCP employs the Google Deployment Manager for writing flexible template and configuration files. Users can utilize a declarative format using YAML, or Python and Jinja2 templates, to configure their deployments effectively.
5.3
Cloud Landing Zone Lifecycle
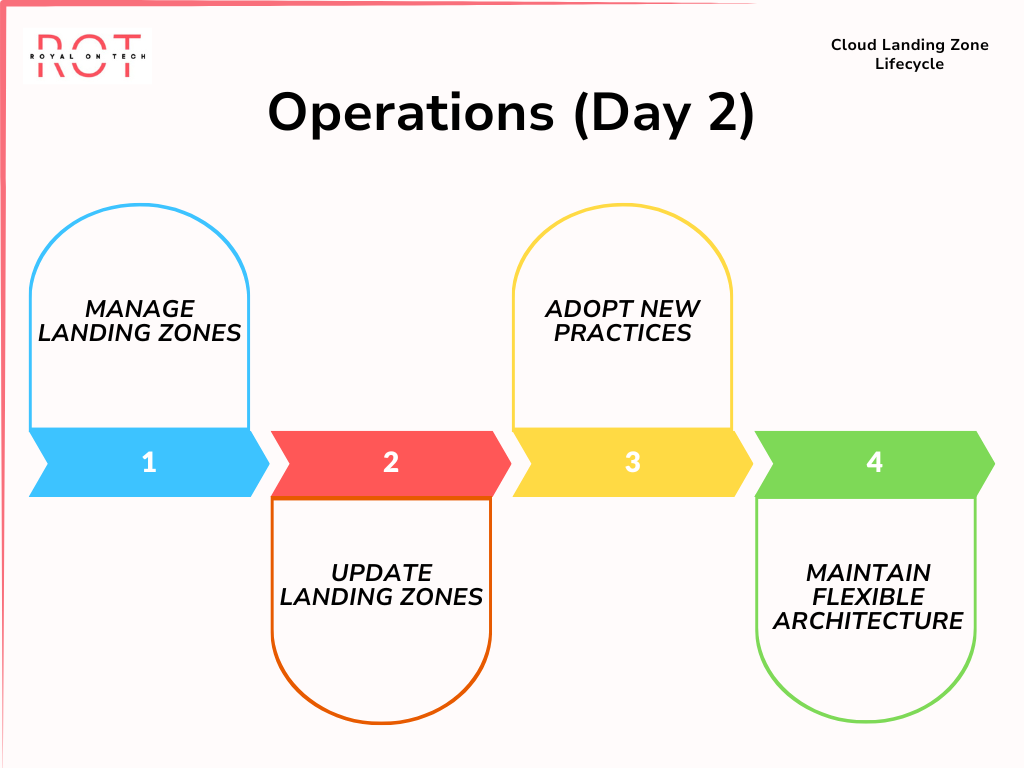
Operations (Day 2)
- Managing the cloud landing zone is an ongoing process. As cloud environments evolve, continuous maintenance and updates are necessary to keep landing zones aligned with best practices. Tools like AWS Control Tower can help manage landing zones effectively.
Operations (Day 2) Explained
Cloud environments are constantly changing, requiring ongoing attention to manage and operate the underlying landing zones effectively.
As your cloud usage grows, it’s essential to maintain and update the landing zones to keep pace with evolving cloud environments.
This involves adopting new best practices from cloud providers, addressing emerging needs stemming from new applications, and responding to evolving security threats.
It’s crucial to ensure that your architecture remains flexible enough to accommodate expansion and updates to the landing zones during ongoing operations.
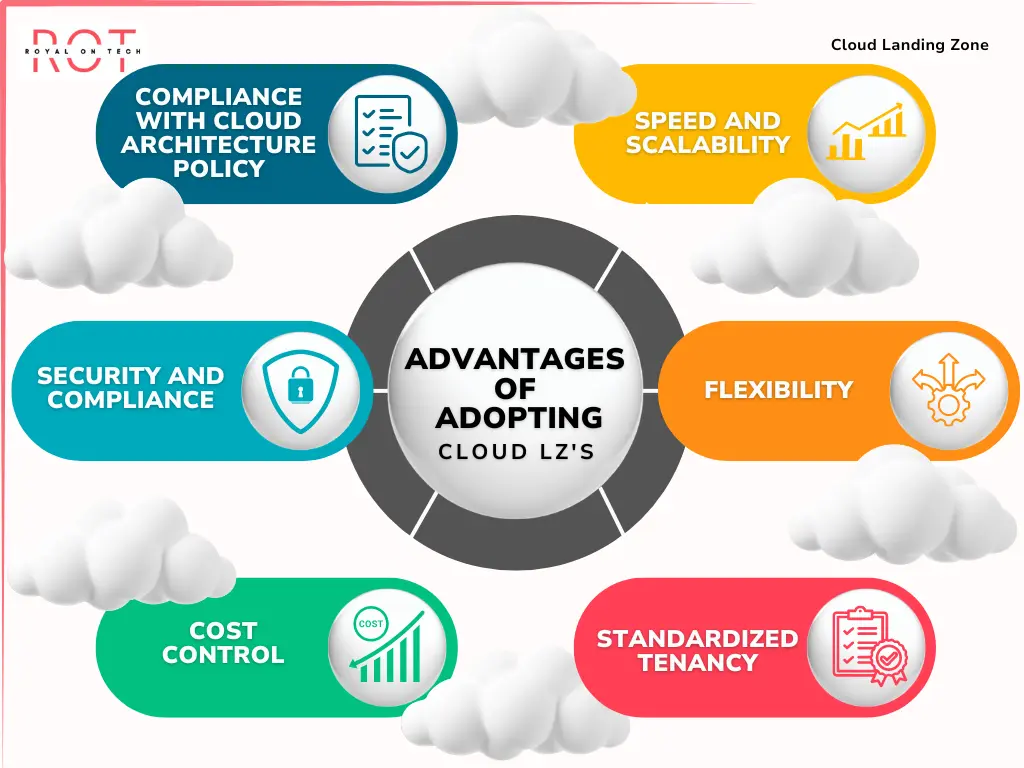
6 - Advantages of Adopting a Cloud Landing Zone
6
Network Security Administrator
Compliance with Cloud Architecture Policy: A well-defined cloud environment minimizes risks and ensures compliance with organizational policies.
Speed and Scalability: Cloud migration becomes faster and more cost-effective with a landing zone, reducing time-to-market and optimizing DevOps processes.
Security and Compliance: Compliance is seamlessly integrated into the landing zone, allowing developers and engineers to work safely and efficiently.
Flexibility: High-degree standardization simplifies the implementation of new applications, enhancing flexibility and scalability.
Cost Control: Landing zones provide transparency in cloud spending, helping organizations avoid unexpected expenses and optimize costs.
Standardized Tenancy: Standardizing tenancy in a multi-tenant architecture allows for better control and enforcement of security policies.
7 - Who Should Be Using Cloud Landing Zone?
7
Cloud landing zones are beneficial for organizations with the following characteristics:
- Lack of clear cloud spending models or central IT architecture.
- Need for rapid migration and deployment of new applications.
- Desire to optimize DevOps processes and reduce time-to-market.
There are many advantages to using a cloud landing zone, but who benefits the most from it?
Two factors are essential in determining which developers and organizations gain the most from it.
Current Cloud Environment
First, consider the organization’s current cloud setup. Developers working with organizations that lack clear insight into their cloud spending, have an unclear DevOps model, or insufficient centralized IT architecture may benefit the most from a cloud landing zone.
Speed and Efficiency
Another key factor is speed. Cloud landing zones enable quick migration, rapid deployment of new applications, faster time-to-market, and streamlined DevOps processes. This is especially useful for developers in fast-paced organizations. Additionally, cloud landing zones can efficiently handle changes such as scaling up or onboarding new employees.
8 - The ROT Perspective on Landing Zones
At ROT, we have a unique approach to the concept of landing zones. Our ROT Landing zones utilize native tools provided by different cloud platforms and vendors. This allows for seamless integration with existing operations and leverages the most powerful, well-integrated tools available on each platform. Often, these tools adhere to the infrastructure-as-code paradigm, which aligns well with ROT’s multi-cloud orchestration strategy.
Day 0 – Design Phase: On the initial setup day, landing zone design is handled using native tools from the respective cloud providers.
Day 1 – Deployment Phase: Once the design phase is complete, ROT takes over the deployment process. For instance, existing Azure blueprints can be integrated into ROT Landing zones. ROT Landing zones harness the power of native tools from various providers, such as AWS’s OU Assignments, Lambda Invocations, and CloudFormation Templates.
Day 2 – Operational Phase: For ongoing operations, ROT offers several tools for managing landing zones. Fast updates across multiple projects enable quick responses to immediate security threats. Long-term development and compliance with new regulations are facilitated by versioning the landing zones. With ROT, you can always track which projects are using which landing zone version across different platforms.
Final Thoughts
A cloud landing zone provides a structured and efficient approach to cloud migration, offering numerous benefits such as improved speed, security, and cost control.
Whether you are accelerating cloud migration or exploring the cloud for the first time, a landing zone establishes a strong foundation for your cloud journey, ensuring resilience, governance, and optimal performance.
FOLLOW US
Technology Partners