For More Info!
Cloud Landing zone
CLOUD LANDING ZONE
Why GCP Landing Zones Are Key to a Successful Cloud Migration: : A Step-by-Step Approach
Table of Contents
As businesses continue to embrace the cloud for agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, establishing a solid foundation in Google Cloud becomes critical.
This foundation, known as a landing zone, serves as the bedrock for deploying, managing, and scaling your Google Cloud infrastructure.
Let’s explore what a Google Cloud landing zone is, why it’s essential, and how to design one that suits your organization’s needs.
1 - What Is a Google Cloud Landing Zone?
A landing zone is a modular and scalable configuration that serves as a foundation for cloud deployments in Google Cloud.
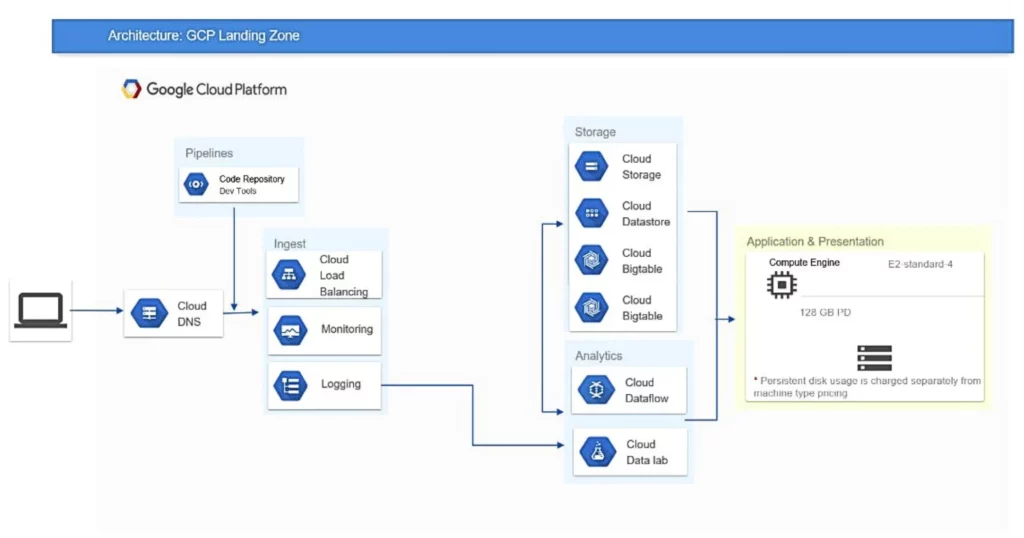
It’s akin to an architectural blueprint, providing best practices, tools, and guidelines to create a secure, efficient, and well-organized environment.
By establishing a landing zone, organizations can adopt Google Cloud with confidence, ensuring governance, security, and cost optimization.
- The diagram is a sample; there’s no standard way to create a landing zone. Design choices will depend on your industry, organization, security needs, intended workloads for Google Cloud, existing IT setup, and business and customer locations.
2 -Why You Need GCP Landing Zone!
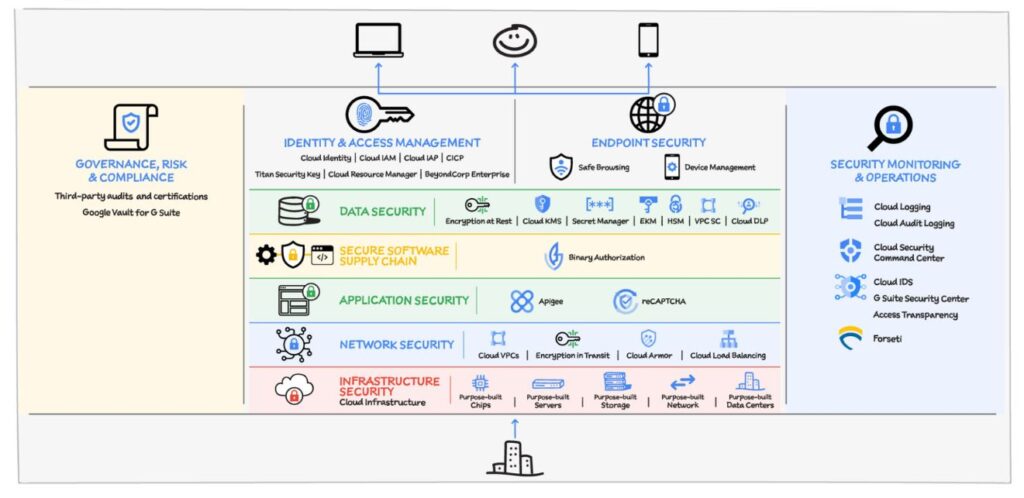
Security and Governance
A landing zone enforces strict controls and access policies, safeguarding your resources and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Consistency and Efficiency
By providing a standardized environment, a landing zone simplifies management and reduces the risk of inconsistencies across projects and teams.
Scalability and Flexibility
A landing zone is designed to support the growth and evolution of your cloud environment, allowing you to adapt and scale as needed.
3 - Optimize Your Cloud Journey with ROT's Google Cloud Landing Zones
ROT’s Landing Zones on Google Cloud Platform provide an efficient solution for businesses to meet their cloud adoption goals. It automates setup, saving time, while ensuring security and scalability.
It’s ideal for establishing new environments or enhancing existing infrastructure, offering features like multi-account architecture and data security.
Cost Control and Optimization
We help identify mismanaged resources, use tools like heat maps, and explore alternatives to maximize cloud benefits.
.
Cloud Adoption
We assist organizations in assessing their cloud journey’s status across people, technology, and processes, guiding them toward their desired destination.
.
Google Cloud Governance
We ensure data security, privacy, usability; GCP governance manages deployment, integration, and security.
Multi-Account Cloud Organization
Our multi-account environment empowers customers to govern and manage securely, facilitating service and product development and enhancement.
4 - Key Elements of a Google Cloud Landing Zone!
A landing zone necessitates designing core elements on Google Cloud, including identity provisioning, resource hierarchy, network, and security controls:
- Resource (Hierarchy) Management
- Identity (Provisoning) & Access Management (IAM)
- Network Design
- Security (Perimeter) Controls
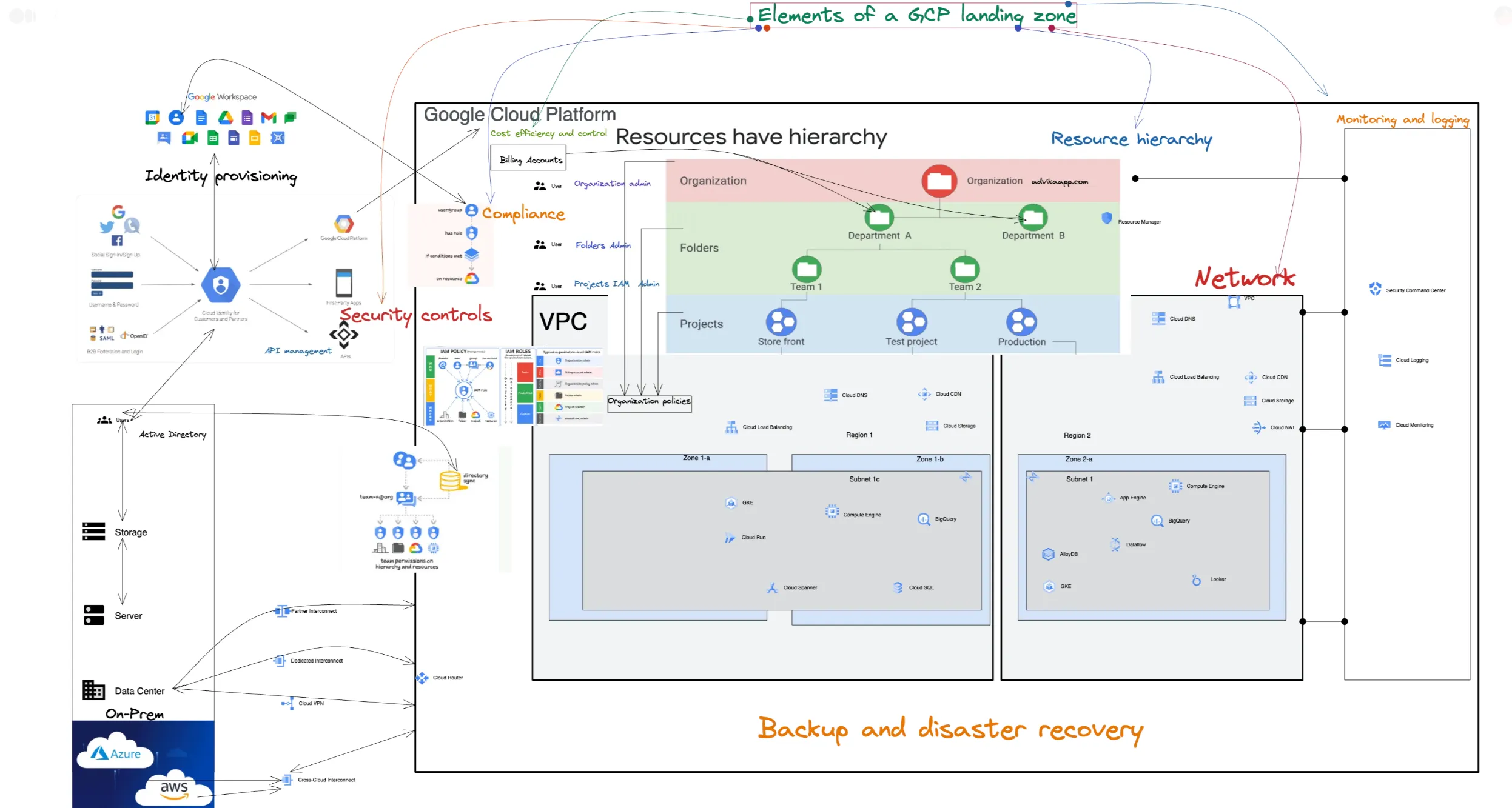
Additionally, consider the following:
- Monitoring and Logging: Develop a strategy ensuring comprehensive data logging, with dashboards for visualization and alerts for actionable exceptions.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Establish a robust strategy for backups and disaster recovery procedures.
- Compliance: Adhere to relevant compliance frameworks pertinent to your organization.
- Cost Efficiency and Control: Implement capabilities to monitor and optimize cost for workloads within the landing zone.
- API Management: Design a scalable API solution, leveraging resources like Apigee API Management.
- Cluster Management: Architect Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters adhering to best practices for scalability, resilience, and observability. Explore resources like GKE best practices and Anthos Service Mesh.
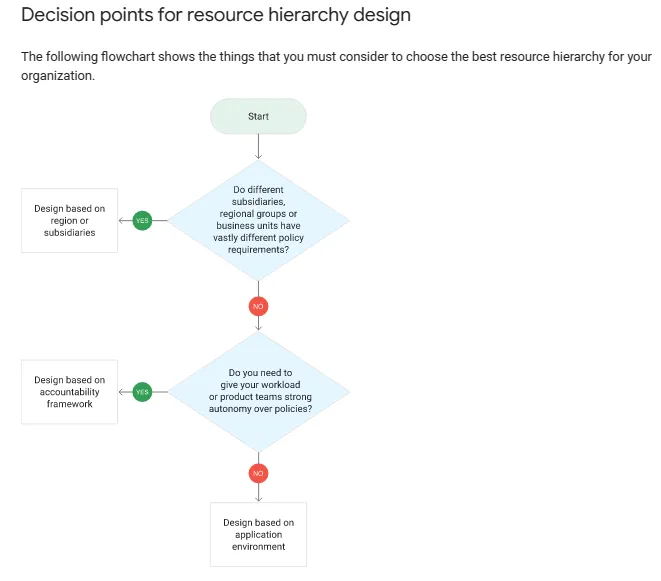
4.1
Resource (Hierarchy) Management
- The Google Cloud Resource Manager allows you to create a structured hierarchy and organizational policies to manage resources efficiently.
Centrally Organize Your Projects
Google Cloud offers resource containers such as organizations, folders, and projects to group and manage your resources hierarchically.
This structure streamlines access control and configuration settings. Resource Manager also allows you to manage these containers programmatically.
Centralized IAM Management
Unify your projects and resources in a Google Cloud organization. Use folders to organize projects by department, team, or application. Update Cloud Identity and Access Management policies at the organization and folder levels to apply changes across projects. Direct project-level adjustments are also possible.
Structured Resource Organization
Organize resources in a hierarchy with the organization as the root. Projects and folders act as children of the organization, while folders can contain projects or other folders. All resources are linked to a project as children. Set access control and configurations at the parent level to inherit settings for child resources.
Manage Projects Efficiently
Programmatically create, manage, and delete projects and folders within your organization. Recover or undelete projects when needed.
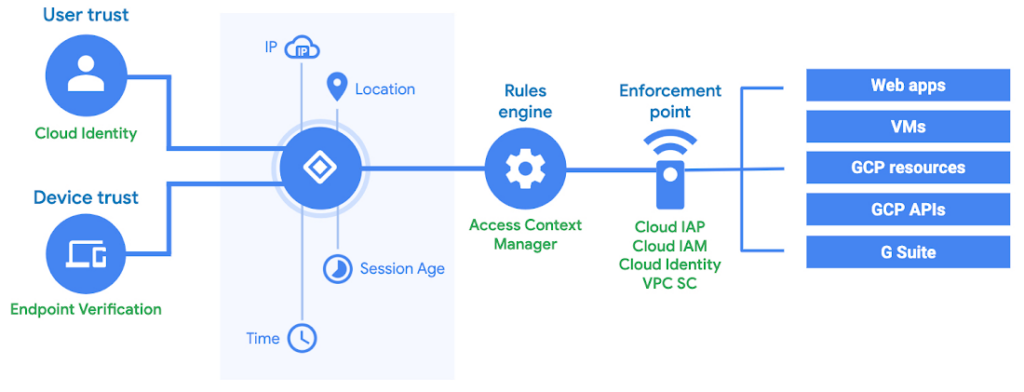
4.2
Identity (Provisoning) & Access Management (IAM)
- Cloud Identity synchronizes with on-premises identity providers, providing granular access controls to your Google Cloud resources.
Simplicity at the Core
IAM understands the complexity of managing organizational structures and permissions that change rapidly. Designed for ease of use, its universal interface streamlines access control across all Google Cloud resources. Learn it once, then apply it everywhere.
Efficient Role Management
IAM simplifies resource permissions with automated tools. Align job functions with groups and roles, ensuring users have access to only what they need. Admins can quickly assign default permissions to entire groups for streamlined management.
Intelligent Access Control
Recommender streamlines permissions management by using machine learning to suggest smart access control changes. It helps admins remove excessive permissions and adjust access based on similar users' behavior, automating the process and improving security.
Granular Context-Aware Access
IAM offers fine-grained control over cloud resource access, beyond just the project level. Set access policies based on attributes like device security, IP address, resource type, and time. These targeted policies enhance security by ensuring appropriate controls are in place for resource access.
Simplify Compliance with an Integrated Audit Trail
IAM provides an automatic audit trail for permissions authorization, removal, and delegation. This feature enables administrators to focus on resource policies and streamlines compliance processes.
Simplify Enterprise Identity
Use Cloud Identity to seamlessly create or sync user accounts across applications and projects in Google Cloud. Manage users, groups, single sign-on, and two-factor authentication from the Google Admin Console. Access Google Cloud Organization for centralized project management with Resource Manager.
Workforce Identity Federation
Workforce Identity Federation uses an external identity provider (IdP) for authenticating and authorizing groups such as employees and partners through IAM. This approach eliminates the need for directory synchronization and simplifies identity management across platforms.
Centralized Organization Policies
Organization Policies sets security guardrails to manage allowed and denied resource configurations, helping you address cloud governance needs. It offers centralized control and granular policies for meeting security and compliance goals.
Plan How to Add Identities to Google Cloud
Users authenticate via Google Sign-In. It’s recommended to onboard users to Cloud Identity or Google Workspace for account lifecycle control.
Decision Points:
- Identity Architecture: Choose Google as primary IdP or federate with external provider.
- Consolidating Accounts: Assess and consolidate existing user accounts.
Options for Identity Architecture:
- Option 1: Use Google as primary source for identities.
- Option 2: Use federation with an external identity provider.
Consolidating Accounts:
- Option 1: Consolidate relevant subset of consumer accounts.
- Option 2: Consolidate all accounts through migration.
- Option 3: Consolidate all accounts through eviction.
Best Practices:
- Select suitable onboarding plan.
- Protect user accounts post-onboarding.
Ensure security for Cloud Identity administrative accounts. Implement uniform multifactor authentication rules. Export audit logs to Cloud Logging.
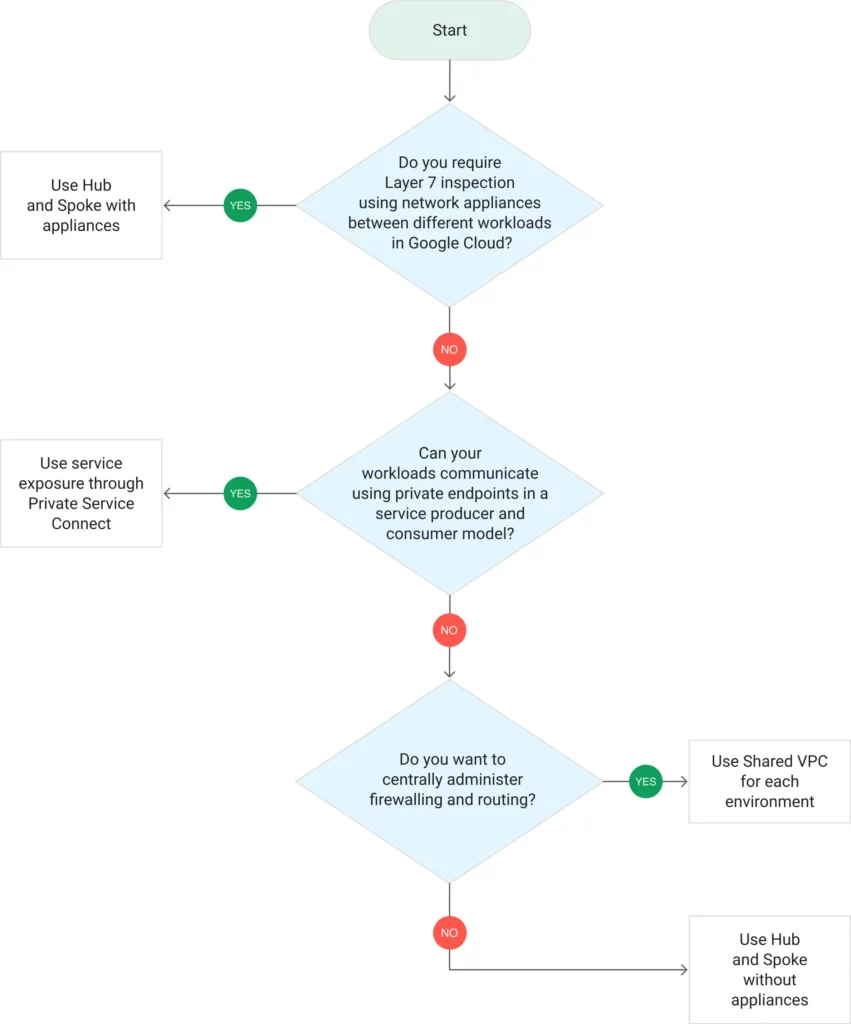
4.3
Network Design
- Choose a network design for your landing zone that aligns with your organization’s needs. This document outlines four common designs, helping you decide based on preferences for centralized or decentralized control. It’s tailored for network engineers and architects involved in crafting your landing zone’s network design.
Key considerations for network design
- Centralized vs. Decentralized Control: Choose between centralized management of IP addressing, routing, and firewalling, or granting teams autonomy to build and manage their own environments.
On-Premises and Hybrid Cloud Connectivity: All designs provide on-premises to cloud connectivity via Cloud VPN or Cloud Interconnect, with some requiring parallel connections and others using a single connection for all workloads.
Security Needs: If centralized network appliances like next-gen firewalls are required, this will shape your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network design.
Scalability: Consider designs that best support your desired number of workloads, VMs, load balancers, and other resources.
Network Design Options
Choose the best network design for your landing zone based on your organization’s needs. We recommend option 1 for most use cases. However, options 2, 3, and 4 offer alternatives for specific scenarios.
- Shared VPC Network for Each Environment: Ideal for central control over network resources and isolation between development, testing, and production environments.
- Hub-and-Spoke Topology with Centralized Appliances: Use this design for Layer 7 inspection and centralized security appliances. It ensures that all traffic between workloads, on-premises, and the internet is inspected and filtered.
- Hub-and-Spoke Topology without Appliances: This design focuses on separating workloads while providing on-premises connectivity. It offers team autonomy over firewall and routing rules.
- Expose Services in a Consumer-Producer Model with Private Service Connect: Each team or workload operates in its own VPC network and uses Private Service Connect to expose services for external access. Choose this option for independent teams and clearly defined endpoints for communication.
Select the option that best suits your needs based on control, connectivity, security, and scalability.
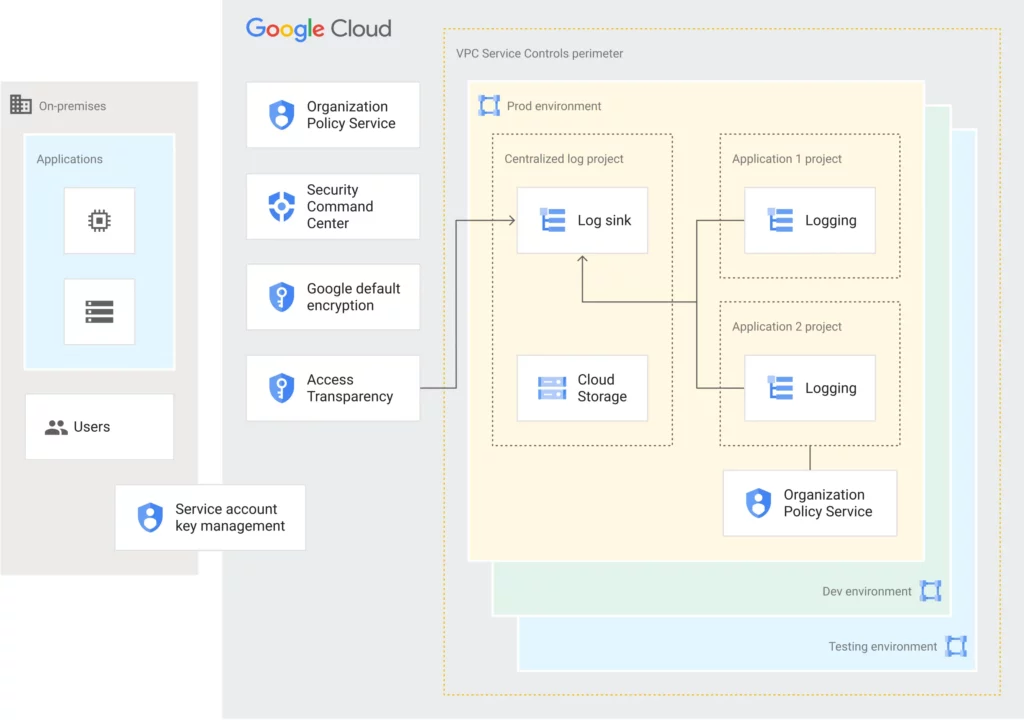
4.4
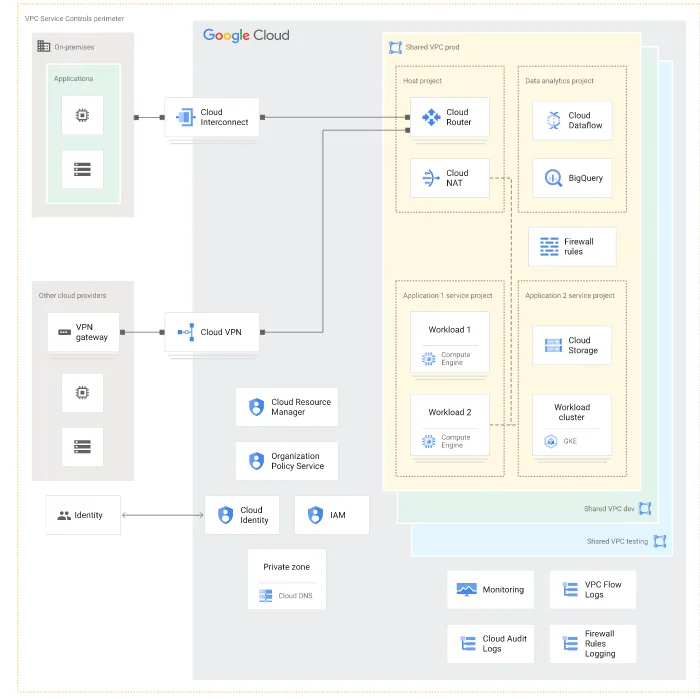
Security (Perimeter) Controls
- This diagram shows aimed at security specialists, CISOs, and architects, providing crucial insights into designing a secure environment on Google Cloud.
Decision points for Security Controls
Limiting Service Account Credentials:
- Avoid freely distributing service account keys.
- Explore alternatives like service account impersonation.
- Consider restricting key creation using organization policies.
Mitigating Data Exfiltration:
- Utilize VPC Service Controls to define perimeters.
- Configure controls broadly or selectively based on data sensitivity.
Continuous Monitoring:
- Activate Security Command Center Premium for real-time insights.
- Monitor for insecure configurations and threats.
Centralized Log Aggregation:
- Configure aggregated log sinks for centralized auditing.
- Centralize audit logs and essential logs for easier monitoring.
Compliance with Encryption:
- Accept default encryption at rest for many use cases.
- Use Cloud KMS for more control over encryption keys.
Encryption in Transit:
- Evaluate default encryption in transit for most traffic.
- Consider additional encryption options like managed certificates.
Managing CSP Access:
- Enable Access Transparency logs to track CSP actions.
- Utilize Access Approval for explicit approval of access requests.
Security Best Practices
In addition to the key decisions outlined above, consider these best practices:
- Provision identities effectively.
- Design a network aligned with your organization’s needs.
- Implement organization policy constraints for added security.
5 - Implement (Network Design) the Solution Using Google Cloud landing zone
When establishing your Google Cloud landing zone, careful consideration of the network architecture is crucial. The network design determines how your resources communicate, access the internet, and interact with each other.
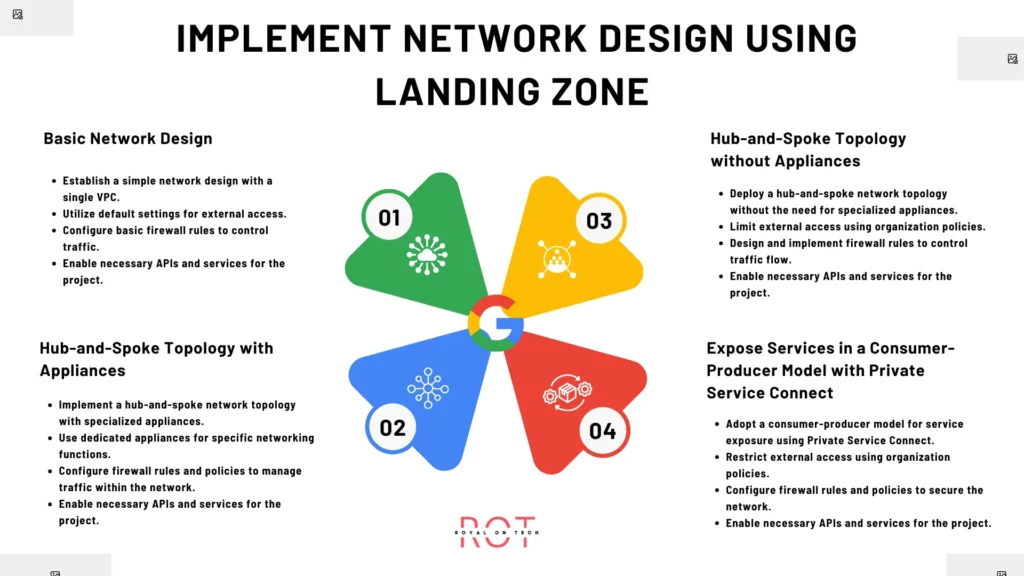
Below are four options for implementing your landing zone network design:
Option 1: Basic Network Design
- Establish a simple network design with a single VPC.
- Utilize default settings for external access.
- Configure basic firewall rules to control traffic.
- Enable necessary APIs and services for the project.
Option 2: Hub-and-Spoke Topology with Appliances
- Implement a hub-and-spoke network topology with specialized appliances.
- Use dedicated appliances for specific networking functions.
- Configure firewall rules and policies to manage traffic within the network.
- Enable necessary APIs and services for the project.
Option 3: Hub-and-Spoke Topology without Appliances
- Deploy a hub-and-spoke network topology without the need for specialized appliances.
- Limit external access using organization policies.
- Design and implement firewall rules to control traffic flow.
- Enable necessary APIs and services for the project.
Option 4: Expose Services in a Consumer-Producer Model with Private Service Connect
- Adopt a consumer-producer model for service exposure using Private Service Connect.
- Restrict external access using organization policies.
- Configure firewall rules and policies to secure the network.
- Enable necessary APIs and services for the project.
Each option offers unique advantages and can be tailored to meet specific requirements, providing flexibility and scalability for your Google Cloud landing zone infrastructure.
Choose the option that best aligns with your organization’s needs and network design preferences. Learn More
6 - Additional Considerations
In addition to selecting one of the four network design options for your Google Cloud landing zone, there are several key considerations to keep in mind to ensure optimal performance, security, and manageability:
Scalability: Design your network with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth and evolving requirements. Utilize features like auto-scaling and flexible IP addressing to adapt to changing workloads and demands.
High Availability: Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure high availability of critical services and applications. Utilize load balancing and multi-region deployments to distribute traffic and mitigate downtime.
Data Encryption: Enforce encryption for data in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Leverage Google Cloud’s native encryption capabilities and key management services for robust data protection.
Compliance and Governance: Adhere to industry-specific compliance standards and regulatory requirements governing data privacy and security. Implement governance policies and audit controls to maintain compliance and accountability.
Monitoring and Logging: Set up comprehensive monitoring and logging mechanisms to track network performance, detect anomalies, and troubleshoot issues proactively. Utilize Google Cloud’s monitoring and logging tools for real-time insights and analysis.
Cost Optimization: Optimize network resources and configurations to minimize costs without compromising performance or security. Implement cost management strategies such as resource tagging, usage analysis, and rightsizing to optimize spending.
Network Segmentation: Segment your network into logical compartments or virtual subnets to isolate workloads, control access, and enhance security. Utilize VPC peering, firewall rules, and network policies to enforce segmentation and access controls.
Disaster Recovery: Develop robust disaster recovery plans and backup strategies to protect against data loss and service disruptions. Implement geo-redundant storage, backup solutions, and disaster recovery automation to ensure business continuity.
Collaboration and Integration: Facilitate seamless collaboration and integration with other cloud services, on-premises systems, and third-party applications. Leverage Google Cloud’s ecosystem of APIs, integrations, and partnerships for enhanced interoperability.
Continuous Improvement: Continuously evaluate and refine your network design and configurations based on evolving business requirements, technological advancements, and best practices. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and innovation to drive ongoing optimization and efficiency gains.
7 - The ROT Perspective on GCP Landing Zones
As part of our journey towards establishing robust infrastructure on Google Cloud Platform (GCP), we, at ROT (Replace with your company name), adopt a comprehensive approach to crafting effective landing zones.
Our landing zone strategy on GCP is tailored to optimize resource allocation, enhance security, and streamline management processes.
Key Principles:
- Resilience: Our landing zones are designed to withstand disruptions and maintain continuity of operations even in the face of failures or outages.
- Optimization: We prioritize resource optimization to ensure cost-effectiveness while delivering optimal performance and scalability.
- Trustworthiness: Security and compliance are paramount. We adhere to rigorous security standards and regulatory requirements to safeguard data and infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Our landing zones are built with flexibility in mind, allowing for agility and adaptability to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Implementation Framework:
- Architecture: We deploy well-architected solutions on GCP, leveraging best practices and design patterns to achieve reliability, scalability, and performance.
- Automation: We embrace automation to streamline deployment, configuration, and management tasks, enabling efficient resource provisioning and maintenance.
- Governance: We establish robust governance frameworks to enforce policies, monitor compliance, and ensure accountability across the organization.
- Monitoring & Optimization: We implement comprehensive monitoring and optimization strategies to track performance metrics, detect anomalies, and optimize resource utilization.
- Continuous Improvement: We foster a culture of continuous improvement, regularly evaluating and refining our landing zone designs to incorporate feedback, lessons learned, and emerging technologies.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Our landing zones provide a secure foundation with built-in security controls, encryption, and compliance mechanisms to protect sensitive data and assets.
- Cost Efficiency: By optimizing resource usage, automating processes, and implementing cost management strategies, we achieve cost savings and maximize ROI on GCP investments.
- Scalability & Agility: Our landing zones are designed to scale seamlessly to accommodate changing workloads and business requirements, enabling agility and innovation.
- Reliability & Performance: We ensure high availability, fault tolerance, and optimal performance of applications and services hosted on GCP, minimizing downtime and maximizing reliability.
- Simplified Management: Through automation, governance, and centralized management tools, we simplify the administration and operation of our GCP landing zones, reducing complexity and overhead.
Final Thoughts
Establishing effective landing zones on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is crucial for a company like ROT. By focusing on resilience, optimization, trustworthiness, and flexibility, ROT can unlock benefits like enhanced security, cost efficiency, scalability, and agility.
Embracing architecture, automation, governance, monitoring, and continuous improvement is key to success. The journey is ongoing, marked by learning and adaptation, but by committing to it, ROT can leverage GCP’s potential for digital transformation and strategic success.
FAQs
What is a GCP Landing Zone?
- A GCP Landing Zone is a foundational setup for hosting workloads on Google Cloud Platform. It provides the necessary infrastructure, networking, security, and governance to support various applications and services.
Why is a Landing Zone Important?
- A Landing Zone ensures a standardized, secure, and scalable environment for deploying workloads on GCP. It streamlines operations, enhances security posture, and facilitates compliance with organizational policies and industry regulations.
What are the Key Components of a GCP Landing Zone?
- Components include networking configurations, identity and access management (IAM) policies, security controls, logging and monitoring mechanisms, billing and cost management setups, and automation tools for provisioning and managing resources.
How is Security Addressed in a GCP Landing Zone?
- Security is addressed through various measures such as identity and access management, network segmentation, encryption at rest and in transit, vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and regular security assessments and audits.
Can a Landing Zone Accommodate Multiple Environments (e.g., Development, Testing, Production)?
- Yes, a Landing Zone can accommodate multiple environments by leveraging resource isolation, role-based access controls, and environment-specific configurations. Each environment can have its own set of resources and policies within the Landing Zone framework.
What Deployment Models are Supported by GCP Landing Zones?
- GCP Landing Zones support various deployment models including single-cloud, multi-cloud, hybrid cloud, and edge computing deployments. They are designed to adapt to diverse infrastructure requirements and use cases.
How Can I Ensure Compliance Within a GCP Landing Zone?
- Compliance within a GCP Landing Zone can be ensured by implementing predefined policies, conducting regular audits, leveraging compliance frameworks, and integrating with relevant compliance tools and services offered by GCP.
What Are Some Best Practices for Managing and Maintaining a GCP Landing Zone?
- Best practices include automating infrastructure provisioning and management tasks, implementing infrastructure as code (IaC) practices, regularly updating security configurations and patches, monitoring resource utilization and performance, and conducting periodic reviews and optimizations.
FOLLOW US
Technology Partners